Содержание
- Difference Between Bug, Defect, Error, Failure, and Fault in Software Testing
- What Is a Bug?
- What Is A Defect?
- Arithmetic Defect
- Syntax Defects
- Logical Defects
- Performance Defects
- Multithreading Defects
- Interface Defects
- What Is an Error?
- What Is a Failure?
- What Is a Fault?
- Why Do People Confuse Between These Terms?
- Bug vs. Defect vs. Error vs. Failure vs. Fault: Differences
- #1. Definition
- #2. Different Types
- #3. Raised By
- #4. Reasons
- #5 How to Prevent Them
- Conclusion
Difference Between Bug, Defect, Error, Failure, and Fault in Software Testing
Software testing is a process to spot bugs, errors, defects, faults, and failures which are the variance between expected and actual results.
Whether you test your software manually or with automated procedures, these terms surface when identifying the issues in your coding.
And by identifying deficiencies, missing requirements, or errors in the software, you are making your software flawless and of high quality for the users.
This way, you can cater to a better user experience as they can easily use the software without any issues and performance or functionality deteriorations.
In this article, I’ll explain what bugs, errors, defects, faults, and failures are and the differences between these terms based on their definitions, types, examples, reasons, focus, and other parameters.
What Is a Bug?
The bug is a widely used term in software development. But, it’s not a welcoming one. It is described as an issue or error that can cause the software to behave in other ways that are not expected by the user or intended by the developer.
Bugs have a vast range of impacts on software performance, from small issues that can easily be managed to the big ones that can make your application impossible to use. But, in both cases, bugs need to be addressed and fixed immediately in order to deliver a quality experience to the users and build trust.
Major bugs are generally treated as prioritized and urgent, especially when there is a risk of user dissatisfaction. There are many bugs that can affect functionality and performance, but the most common type of bug is crash. This means the software stops working as expected by the users and shuts downs automatically in the middle of use.
For example, when a user writes a report or article in a word processing software, and it crashes suddenly, the user will lose all the work if they don’t press the save button before. This will have a negative impact on the productivity of the user.
Typos are also bugs that seem to be tiny issues but are capable of creating disastrous results. Even an incorrect number or a misplaced letter can cause a drastic change to a program’s intended functions.
In addition, a software bug disrupts an organization’s ability to interact with users, generate leads, facilitate purchases, and more. Thus, it must be eradicated as soon as possible.
What Is A Defect?
A defect in software testing refers to the deviation or variation of the software from the users or business requirements. It is an issue in application coding that can affect the whole program. Testing teams, while executing different test cases, come across defects.
Defects in a product represent the inefficiency and inability of the application to meet the criteria and prevent the software from performing the desired work. These happen during the software development cycle by developers. A defect can form when a programmer or developer makes some minor or major mistake during the development phase.
Well, bugs and defects have very thin differences. In the software industry, both are considered faults that need to be fixed immediately before deployment. There are many types of defects that you can come across during the software development cycle. They are as follows:
Arithmetic Defect
An arithmetic defect includes defects in the arithmetic expression or finding solutions to some arithmetic expression in the program. These mistakes are caused mainly by the developers working on the software due to less knowledge or excess work. Code congestion is also a reason for arithmetic defects when developers are unable to watch the code correctly.
Syntax Defects
Syntax defects are the common types of mistakes made while writing code. It shows even a minor error in the syntax. This occurs when a developer or programmer mistakenly escapes a symbol in the program, such as a semicolon (;), while writing code in C++.
Logical Defects
Logical defects come into the picture during the implementation of the code. When a programmer thinks incorrectly about the solution or doesn’t understand the requirement clearly, these defects happen. It also occurs when a developer forgets about the corner cases. It is related to the core of the application.
Performance Defects
When the software application or system is unable to meet the expected results, it’s referred to as a performance defect. It includes the response of the application during use with varying loads.
Multithreading Defects
Multithreading defects happen when executing or running multiple tasks at the same time. This can lead to the possibility of complex debugging. During the multithreading process, there is a chance of deadlock and starvation that results in the system’s failure.
Interface Defects
Interface defects are the defects that occur during the interaction of users and software. It includes complicated interfaces, platform-based interfaces, or unclear interfaces. These defects prevent users from utilizing the software effortlessly.
What Is an Error?
An error is a misconception, misunderstanding, or mistake on the part of the application developer. A programmer or developer can sometimes misunderstand the sign notation or might type a wrong spell, resulting in an error in the programming code.
It is generated due to wrong logic, syntax, or loop that can impact the end-user experience significantly. In basic terms, an error is calculated by differentiating between the expected results and actual results. Inside a program, when such a scenario comes, it changes the application’s functionality, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
An error raises due to several reasons but leads to an issue in the application code. It can be design issues, coding issues, or system specification issues. It is slightly different from defects.
Functionality is a major criterion of software, but sometimes, the software leads to functionality errors when something is awkward, impossible, confusing, or harder. Types are errors are:
- Communication errors can occur during communication from the application to the user. For example, no menu provided in the software, no help instructions, no save button, etc.
- Missing command error is another common error among programmers due to low typing speed, short deadlines, or more. The output of the program deviates if some commands are missing.
- Grammatical incorrect sentences and misspelled words are common errors found in every application code. When the error is handled in a meaningful and transparent manner, it can be reduced during testing.
- Calculation errors occur due to coding errors, bad logic, incorrect formulae, function call issues, data type mismatch, and more.
What Is a Failure?
Sometimes during the execution of the program, the system will produce unexpected results that can lead to application failure. Under certain situations or environments, defects can be the reason for failure, and sometimes the reasons may vary.
Not every defect results in failures. For example, defects in the dead code will not result in failures. It can also be caused due to other reasons. Furthermore, many a time, environmental conditions, including a strong magnetic field, pollution, electronic fields, radiation burst, etc., can cause failure in the firmware or hardware.
Failure can also happen due to human errors while interacting with software. For example, a software failure can occur if a human puts a wrong input value. However, a failure can also be caused intentionally in the system by an individual.
When it comes to software failures, there are a few points that are essential for you to understand:
- During software testing, if a tester is not sure whether a given situation is a failure or not, it can be referred to as an incident. The incident then requires further testing to confirm whether the defect is the cause of the failure or some other reasons like invalid input, unfavorable environment, and lack of knowledge on its functionality.
These incidents are reported and sent to developers so that they can analyze the incident to confirm the reason for failure.
- Failure is a term that comes after the production stage of the software. To judge the quality of the software, it needs to be checked properly before deployment since quality holds the utmost importance in increasing customer confidence, resulting in enhanced business.
However, failure can only be identified in the application when the defective part is executed. If the defective parts have not been executed at all, that part can’t cause any failure.
What Is a Fault?
A fault is an unintended or incorrect behavior by an application program. It causes a warning in the program. If it is left untreated, it may lead to failures in the working of the deployed code. If various components of the application code rely on each other, a fault is the one that may cause problems in multiple components.
A minor fault can result in a high-end error. The fault can be prevented by adopting programming techniques, development methodologies, peer review, and code analysis.
Here are various types of faults in software testing, such as:
- Algorithm fault: It occurs when a component logic or algorithm is unable to provide a clear result for the given input because of wrong processing steps. But, it can be easily prevented by disk checking.
- Syntax fault: It occurs when using the wrong syntax in the code. A single syntax error can result in zero output or failure.
- Computational fault: It occurs when a disk implementation is wrong or is unable to calculate the desired result. For example, combining floating point and integer variables may produce an unexpected result.
- Timing fault: When the application is not responding after the program fails, it is called a timing fault.
- Documentation fault: Proper documentation tells what the program actually does. Documentation fault occurs when the program doesn’t match with documentation.
- Overload fault: Developers use data structures like a queue, stack, and array for memory purposes in the programs. When the user fills the memory and uses it beyond its capacity, it will lead to an overload fault.
- Hardware fault: When the specified hardware doesn’t work properly for the desired software, this type of fault occurs.
- Software fault: When the specified software is unable to work or support the platform or operating system, this type of fault occurs.
- Omission fault: When the key aspect is misplaced or missing in the program, omission fault occurs. For example, initialization of the variable is not done at the starting point.
- Commission fault: When an expression statement is wrong, commission fault occurs. For example, an integer is initialized with float.
However, implementing suitable techniques can easily avoid a fault in the program. These techniques and procedures are needed to be aligned with intended software and hardware specifications, programming languages, algorithms, etc.
Why Do People Confuse Between These Terms?
Bug, defect, error, failure, and fault are often used as synonyms in general terms. But software testing has differences according to their behavior.
An error is a mistake that is done by a developer. A defect is called an error that is found during the development cycle. A bug is a defect that is found during the testing cycle. A failure is termed when the program doesn’t meet the criteria. A fault is the cause of failure.
However, these terms are used differently to define the issues in the code.
Let’s understand these terms by using a real-life example:
Imagine your car that is not working, and you take it to a mechanic. You complain that the car is not running (the user reports a failure). The mechanic inspects the car and figures out the issue (defect). The issue (error) was that the driver put diesel in the gasoline engine (the tester identified the failure) – it was the user’s fault.
Bug vs. Defect vs. Error vs. Failure vs. Fault: Differences
Now that you have some ideas about these terms, let’s understand some key differences between them in software testing:
#1. Definition
A bug refers to defects, telling the software is not working as expected. A defect is a deviation between the expected and actual output. An error is an issue or mistake made by the developer during writing the code due to which compilation and execution fail.
Failure is the combination of various defects that leads to hardware and software failure resulting in an unresponsive system. A fault is the one causing the software to fail and preventing it from performing the intended tasks.
#2. Different Types
Types of bugs are logical bugs, resource bugs, and algorithmic bugs. The defect is classified as critical, minor, major, and trivial. Types of errors are syntactic error, UI screen error, flow control error, hardware error, calculation error, and more. Types of faults are business logic faults, logical faults, functional faults, GUI faults, security faults, hardware faults, and more.
#3. Raised By
A bug is raised by test engineers. The defect is identified by test engineers and is resolved by programmers or developers. Automation test engineers and developers raise errors. The testers find the failure during the development phase. Users find the faults.
#4. Reasons
The bug is caused due to missing logic, redundant codes, and erroneous logic. The defect is caused due to providing incorrect input, errors in coping, and more. The error is caused due to code error, inability to execute, ambiguity in code logic, faulty design, logical error, etc. The failure is caused due to system errors, human errors, and environmental variables. The fault is caused due to wrong design, irregular logic, and more.
#5 How to Prevent Them
To prevent bugs, you need to implement test-driven development, adjust enhanced code development practices, and more. To prevent defects, you need to implement out-of-the-box programming methods and use correct and primary software coding practices.
To prevent errors, you need to conduct peer reviews, validate bug fixes, enhance the overall quality of the application, and more. To prevent failure, you need to confirm the re-testing of the process, review the requirements, categorize the issues, and evaluate the errors.
To prevent faults, you need to review the documents and verify the application design and coding correctness.
Conclusion
Bugs, defects, errors, failures, and faults affect different parts of an application and impact its usage massively. These slow down the performance and excellence of the software, resulting in customer dissatisfaction.
Hence, these issues must be prevented in any software project immediately, so your software performs optimally and its demand remains at the top of the market.
You may also look at some of the Software testing tools.
Источник
We use the software in day-to-day life, such as at home, work, banking, shopping, etc. However, at times, the software does not work as expected. For instance, website not loading correctly, an error on a bill, a delay in credit card processing, are typical examples of problems that may happen because of errors, defects, and failures in the software. Today we will discuss the common terminologies that we use when software doesn’t work as expected, i.e., Error, Defect, and Failure.
- What is Error, Defect, and Failure?
- What are the causes of Errors in Software?
- Not all unexpected test results are failures
- What are Defects, Root Causes, and Their Effects?
Introduction to Error, Defect, and Failure
Let’s try to understand the inter-relation between Error, Defect, and Failure:
It is well said by Thomas Muller “A person can make an error (mistake), which produces a defect (fault, bug) in the code, in software or a system, or a document. If the execution of the defect in code happens, the system will fail to do what it should do (or something it shouldn’t), which causes a failure”.
Let’s take an example of an organization that developed a new application named «Saff Promotion System» for their annual appraisal. But employee satisfaction even after the appraisal was low. Because they considered it not up to the mark. The management, then, decided to analyze the root cause of this dissatisfaction.
Therefore, they backtracked the process and found that the software marked full day leave for the employees who reached office after 10 a.m. This was due to some coding errors. The tester also skipped these errors in coding. So, the software with this defect went to production. Which, in turn, caused a general degradation and failure of the system.
The figure below shows the interrelation between Error, Defect, and Failure.
Errors:
The Error is a human mistake. An Error appears not only due to the logical mistake in the code made by the developer. Anyone in the team can make mistakes during the different phases of software development. For instance,
- BA (business analyst) may misinterpret or misunderstand requirements.
- The customer may provide insufficient or incorrect information.
- The architect may cause a flaw in software design.
- People on the team can also make mistakes due to unclear or insufficient requirements, time pressure, lethargy, or other reasons.
Let us observe the basic types of errors in software testing:
Types of Error
- User Interface Error: These are the errors that generally appear during user interaction with the system. Such as missing or incorrect functionality of the system, no backup function or reverse function available, etc.
- Error handling error: Any error that occurs while the user is interacting with the software needs precise and meaningful handling. If not, it confuses. Therefore, such errors are known as error handling errors.
- Syntactic error: Misspelled words or grammatically incorrect sentences are Syntactic errors and are very evident when testing the software GUI.
- Calculation errors: These errors occur due to bad logic, incorrect formulas, mismatched data type, etc.
- Flow control error: Errors concerning passing the control of the program in an incorrect direction where the software program behaves unexpectedly are flow control errors. Such as the presence of an infinite loop, reporting syntax error during run-time, etc.
- Testing errors: It implies the errors that occurred when implementing and executing the test process. For example, bug scanning failure, inefficiency in reporting an error or defect.
- Hardware errors: Such errors are related to the hardware device. Such as no availability and no compatibility with the device.
Defect:
A Defect is a variance between expected and actual results. An Error that the tester finds is known as Defect. A Defect in a software product reflects its inability or inefficiency to comply with the specified requirements and criteria and, subsequently, prevent the software application from performing the desired and expected work. The defect is also known as Fault.
Types of defects:
Severity Basis:
Severity defines the degree of impact. Therefore, the severity of the defect reflects the degree or intensity of a particular defect to adversely impact a software product or its operation. Based on the severity metric, a defect falls under the following categories:
- Critical: Defects that are «critical» require immediate attention and treatment. A critical defect directly affects the essential functionalities which can otherwise affect a software product or its large-scale functionality. For instance, failure of a feature/functionality or collapse of the entire system, etc.
- Major: Defects, which are responsible for affecting the main functions of a software product are Major Defects. Although, these defects do not result in the complete failure of a system but may bring several primary functions of the software to rest.
- Minor: These defects produce less impact and have no significant influence on a software product. The results of these defects are visible in the operation of the product. However, it does not prevent users from executing the task. The task can be carried out using some other alternative.
- Trivial: These types of defects have no impact on the operation of a product. Hence, sometimes, we ignore and omit them. For example, spelling or grammatical errors.
Probability Basis:
One more angle to see a defect in a software application is the probability that it will occur, and chances that the user will find it. Depending on the likelihood or the possibility of a defect in a software product in terms of percentage is classified in the following ways:
- High: Almost all users of the application can track the presence of defects. This indicates a high probability.
- Medium: Half of the users can trace the presence of defects in a software product.
- Low: In general, no user detects it, or only a few users will be able to detect it.
Priority Basis:
Defects also have a business perspective comparison. The rectification of some defects must happen first. Likewise, some can solve at a later stage. Just like a business where everything happens according to the current need and demand of the market. Just like the probability base, priority classification also occurs in the following ways:
- High: The high priority defines the most critical need of a company to correct a defect. This should happen as soon as possible, in the same compilation.
- Medium: Medium priority defects are next to high priority. And any next version or release of a product includes addressing them.
- Low: This type of defect does not need to be corrected individually. Consideration of repairing these types of defects, along with any other defects is voluntary.
Failure:
Failure is a consequence of a Defect. It is the observable incorrect behavior of the system. Failure occurs when the software fails to perform in the real environment.
In other words, after the creation & execution of software code, if the system does not perform as expected, due to the occurrence of any defect; then it is termed as Failure. Not all Defects result in Failures; some remain inactive in the code, and we may never notice them. Failures also occur due to the following reasons:
- Any physical damage or overheating in the hardware can cause the whole system to fail.
- If the software is not compatible with the hardware, then also the system performs unexpectedly.
- Failures also happen by environmental conditions like a radiation burst, a strong magnetic field, electronic fields, or pollution could cause faults in hardware or software.
Not all unexpected test results are failures:
Failures can also
- Happen due to a human error in interacting with the software, like entring an incorrect input value, or misinterpreting an output.
- Occur when someone deliberately tries to produce system failure or cause malicious damage.
- Happen because of the mishandling of test data, test environment, etc. Such conditions are known as defects, but they aren’t actually a Defect.
- Sometimes, tests that result in undetected defects can also cause failure.
What are the causes of Errors in Software?
Here we will discuss some possible causes of these errors.
- Time pressure: At times, software development happens under limited / insufficient resources with unrealistic deadlines. Developers do not have enough time to test their code before delivering it to the testing team. Which, in turn, introduces errors.
- Human fallibility: Human beings are prone to make mistakes. It would be foolish to expect the software to be perfect, and without any flaws in it! Ironically, we have not yet discovered any other non-human agent that can develop software better than humans. Therefore, we continue to rely on human intelligence to develop software. Thereby, increasing the possibility of errors in it.
- Inexperienced or insufficiently skilled project participants: Allocation of correct work to the correct resource is fundamental for the success of any project. Team members should be assigned a task according to their skills and abilities. An inexperienced project participant may make mistakes if they don’t have proper knowledge of the work. For example, a resource having a good understanding of the database but having limited knowledge of HTML/CSS is not suitable for designing a website.
- Miscommunication between project participants: Improper coordination & poor communication between various departments in a project can result in disrupted progress. Conflicts can arise each time a project participant misinterprets or misunderstands the words or actions of another. For example, the business analyst does the requirement gathering, and then some other team member does the documentation of the requirements. Any miscommunication between the two can lead to incomplete/wrong requirement document, which, in turn, affects the design of the project.
- The complexity of the code, design, architecture, or the technology to be used: As the complexity of the program, concerning code, design or technology increases, the software becomes more critical and more bugs appear. It is because our brains can only deal with a reasonable amount of complexity or change. Our minds may not be able to process complex information like the form of design, architecture or technology, etc. Therefore, resulting in low quality and erroneous coding.
- Misunderstandings about intra-system and inter-system interfaces: There are high chances of error while establishing an intra-system, and inter-system interfaces. Let’s try to understand what is intra-system and inter-system interfaces mean:-
- Intra-system interface- It implies the integration of different modules/features within a system/application. For example, in an online shopping portal, we have three modules: online order, shipping, and supply chain. These three modules form the intra-system for the online shopping portal. When these different modules are combined, there is a possibility of errors in the final product.
- The inter-system interface- It is the compatibility of an application with other applications when operated together. For example, compatibility between smartphones and tablets while data transfer via Bluetooth.
- New, unfamiliar technologies: Sometimes, the developers and testers need to develop an application using a technique that is unknown to them. Lack of proper knowledge and understanding can lead to errors. At that time, they require a certain level of R & D, brainstorming, and training to reach a reliable solution.
- Environmental conditions: Natural disasters, such as outbreaks of fires, floods, lightning, earthquakes, etc. can affect the computers. For example, a system may not work correctly if the software inside is affected by radiation, electromagnetic, or pollution.
After going through this article, I am sure you will agree with me that various problems and discrepancies encountered during the software process are interdependent and interconnected. Generally, the appearance of one leads to the introduction of another. Which, in turn, affects the functionality of the software and thus, leads to unexpected results.
Most of these terms- error, defect, fault, failure and bugs are used interchangeably but there is difference between them. Some of these terms are very much different from others.
Error
An error is a mistake made by human that leads to discrepancy between the actual and the expected result.
Defect
A defect is a problem in the functioning of a software system during testing. ISTQB defines a defect as “A flaw in a component or system that can cause the component or system to fail to perform its required function, e.g., an incorrect statement or data definition.”
Fault
A fault is an incorrect step, process or data definition in a software product.
Bug
A bug is a flaw in a software system that causes the system to behave in an unintended manner.
Failure
A failure is the inability of a software system to perform its operations within the specified performance benchmark. As per ISTQB, “a defect, if encountered during execution, may cause a failure of the component or system”.
So, we can say that a mistake made by humans during coding is called error, an error found during the testing phase is called a defect, a defect to be resolved by the development team is called a bug and when a build does not meet its specifications then it is termed as failure.
More Difference Between
| Manual vs Automation Testing | Smoke vs Sanity Testing |
| White-box vs Black-box Testing | System vs Integration Testing |
| Verification vs Validation | Quality Assurance vs Quality Control |
| SDLC vs STLC | Test Plan vs Test Strategy |
| Test Case vs Test Scenario | Agile vs Waterfall Model |
| Agile vs Scrum Methodology | REST vs SOAP Web Service |
| Web Application vs Desktop Application | Web Service vs Website |
| Assert vs Verify | Error, Defect, Fault, Failure & Bug |
Kuldeep is the founder and lead author of ArtOfTesting. He is skilled in test automation, performance testing, big data, and CI-CD. He brings his decade of experience to his current role where he is dedicated to educating the QA professionals. You can connect with him on LinkedIn.
Improve Article
Save Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Software Testing defines a set of procedures and methods that check whether the actual software product matches with expected requirements, thereby ensuring that the product is Defect free. There are a set of procedures that needs to be in mind while testing the software manually or by using automated procedures. The main purpose of software testing is to identify errors, deficiencies, or missing requirements with respect to actual requirements.
Software Testing is Important because if there are any bugs or errors in the software, they can be identified early and can be solved before the delivery of the software product.
Here we will discuss 5 terms related to SDLC:
- Bug: A bug refers to defects which means that the software product or the application is not working as per the adhered requirements set. When we have any type of logical error, it causes our code to break, which results in a bug. It is now that the Automation/ Manual Test Engineers describe this situation as a bug.
A bug once detected can be reproduced with the help of standard bug reporting templates. - Defect: A defect refers to the situation when the application is not working as per the requirement and the actual and expected result of the application or software are not in sync with each other.
- Fault: Sometimes due to certain factors such as Lack of resources or not following proper steps Fault occurs in software which means that the logic was not incorporated to handle the errors in the application. This is an undesirable situation, but it mainly happens due to invalid documented steps or a lack of data definitions.
- Failure: Failure is the accumulation of several defects that ultimately lead to Software failure and results in the loss of information in critical modules thereby making the system unresponsive. Generally, such situations happen very rarely because before releasing a product all possible scenarios and test cases for the code are simulated. Failure is detected by end-users once they face a particular issue in the software.
- Error: Error is a situation that happens when the Development team or the developer fails to understand a requirement definition and hence that misunderstanding gets translated to buggy code. This situation is referred to as an Error and is mainly a term coined by the developers.
A simple diagram depicting Bug vs Defect vs Fault vs Failure:
Bug vs Defect vs Error vs Fault vs Failure:
Some of the vital differences between bug, defect, fault, error, and failure are listed in the below table:
| Basis | Bug | Defect | Fault | Error | Failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A bug refers to defects which means that the software product or the application is not working as per the adhered requirements set | A Defect is a deviation between the actual and expected output | A Fault is a state that causes the software to fail and therefore it does not achieve its necessary function. | An Error is a mistake made in the code due to which compilation or execution fails, | Failure is the accumulation of several defects that ultimately lead to Software failure and results in the loss of information in critical modules thereby making the system unresponsive. |
| Raised by | Test Engineers | The defect is identified by The Testers And is resolved by developers in the development phase of SDLC. | Human mistakes lead to fault. | Developers and automation test engineers | The failure is found by the test engineer during the development cycle of SDLC |
| Different types |
|
Defects are classified as follows:
Based on Severity:
|
|
|
NA |
| Reasons behind |
|
|
|
|
|
| Way to prevent the reasons |
|
|
|
|
|
Definitions and Meaning: Error, Fault, Failure and Defect
December 06 10:00 2011 Print This Article
Note: the article was updated in March 2019.
The assurance of continuous software functioning is based on the absence of all possible errors, defects, failures and faults, commonly named in testing terminology as bugs. Even if the impact of some bug is inevitable, it is always possible to reduce the probability of its effect on the program and its processing. Project managers should clearly understand the software testing terminology to lead effective business communication and proper quality control. The article discloses such notions as defect, error, failure and fault to provide QA specialists with reliable guidance.
Types of system bugs with examples
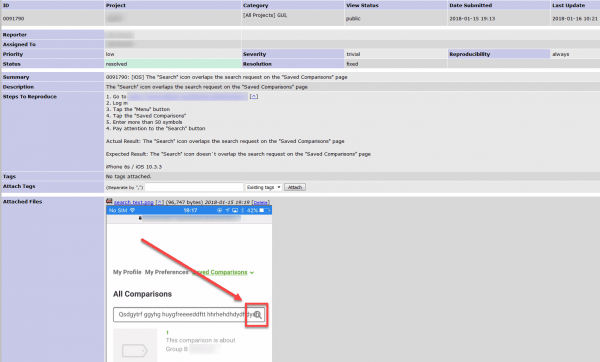
Defect is a drawback, which usually forms at the stage of software production and does not allow to perform the function properly or ruins the entire functionality. Usually, it is identified as an error, which is found after the software release on the market. It may be not sufficient detail, which is noticeable during the processing of a certain function or it may be a critical feature of the entire program, which leads to improper performance of software functions. Below is the example of a bug report:
To sum up, a defect is an unexpected result of software implementation, which differs from the initially required purpose and reduces the value of functions.
One Ends…. and Another Starts
Failure is an impossibility to start the performance of the functions or breach of the program processing after its successful start. The failure may be caused by:
- improper downloading;
- uncompleted downloading;
- improper/breached installation;
- incomplete/breached installation.
Moreover, failures may be the result of intentionally planned illegal penetration into a digital system in the form of cyber-attack with the aim to acquire protected data or to sabotage the work of a system.
Fault is a reason, which enables the software defects to arise. This may be a condition, which is independent from technical peculiarities, but caused by misunderstanding and users mistakes. Fault can be considered as a source of all mentioned bugs and as a result of error, at the same time.
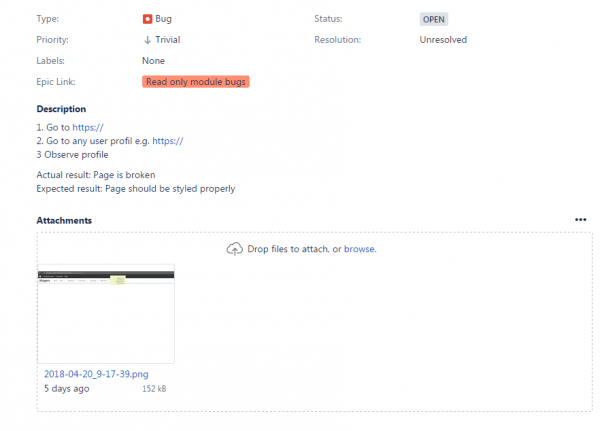
Error is a wrong procedural act, which is caused by improper running of the program or by users’ mistake. Error interrupts or stops the work of software and its appearance usually depends on program settings and its compliance with the device. Below is the example of a bug report written in JIRA:
The reason of these drawbacks may be caused by internal defects of the program, that were formed during its creation or by external factors, such as:
- high load on the device;
- energy and internet connection breaches;
- harmful programs (viruses);
- mismatch of device and software requirements.
In case of external impact, the problem can be solved by:
- simple restart of the program;
- reconnection;
- adjusting of the settings.
However, the internal software issues can be mostly fixed with improvement of the software architecture and removing of coding mistakes.
Possible consequences of missed errors
The drawbacks of software can cause the sufficient business losses due to the delays in the software performance. There is also a threat of misrepresentation or disclosure of confidential data or its complete loss, if such data was involved in the work of a software, that was subjected to error. The most common errors are:
- The user is not able to login into the application.
- A developed feature is missing in the build ‘or’ completely failed.
- Internal Server error during the access to the application.
- Error while customer is making the payment, in case of an eCommerce site.
- Some security permission is required to access a major functionality/application under test.
- The application refuses to run or stops in-between.
These are not abstract suggestions. There are quite famous real cases, when error brought its impact from a digital environment to real life.
For example: a bug causes Uber notifications to be pushed to a device, even after logging out of your account on that device. In this case, the “cheating user”, who had once called Uber from his wife’s phone, was exposed when she received notifications of using Uber. Quite problematic, isn’t it?
Another example shows much more critical case: in January 2018, the citizens of Hawaii were notified to take immediate cover in the face of an inbound ballistic missile strike. It turned out to be a false alarm due to the “troubling” design flaws in the Hawaii Emergency Management Agency’s alert origination software.
Summing It Up
The most effective way to prevent possible bugs is careful professional testing of software with clear understanding of QA testing terminology before its practical implementation. The bugs which were identified can be removed by strict analysis and improvement of code structure of the program, as an initial source of errors. Even if the errors were successfully investigated, it would be more effective to conduct regression testing after the identification of errors and bugs.
Learn more from QATestLab
In this brief testing tutorial, we’ll describe the difference between Defect, Error, Bug, Failure, and Fault.
Software testing lays down the mechanism for finding defects in an application, product or system. A Defect is a deviation between the actual and expected outcomes. A mistake in the source code indicates Error. The error uncovered by a tester becomes a Defect. The defect recognized by the dev team turns into a Bug. If a product build doesn’t pass the acceptance criteria, then it proves to be a Failure.
Hence, all these testing terms revolve around the defect. Let’s understand it in more details.
Defect In Manual Testing
A defect is an anomaly which causes a deviation between the expected and actual results. It could be an error discovered once the application got deployed into production. Some software could show potential issues with both the internal and external features. Hence, any variance in the behavior of the functionalities of a product or software got to be a defect in manual testing.
Check out 100+ manual testing interview questions for Software testers of all experience levels.
Defect Vs. Wrong, Miss, Error, Bug, Failure, and Fault
In Software Testing, Defect has many names such as Wrong, Miss, Error, Bug, Failure, and Fault. Let’s find out what all of these are:
1. Wrong-
Wrong indicates the incorrect implementation of the customer requirements. A manual tester will record it as a defect because of the deviation from the given specification.
2. Miss-
Miss shows that one or more customer requirements got missed in the implementation. It is also a deviation from the original specifications. The tester would also log it as a defect to
3. Error-
An error could arise because of a coding mistake by the developer, he misunderstood, or the requirement was not clear enough. For example, a developer may misinterpret a design flow, or he might use an incompatible data type which results in an Error. Some actions like insufficient array limit, loop getting into the infinite loop or invalid syntax cause to errors. If a tester catches any of these, then he or she will log a defect for the same.
4. Bug-
A bug occurs because of some coding error and leads a program to malfunction. It may also lead to a functional issue in the product. These are fatal errors that could block a functionality, results in a crash, or cause performance bottlenecks. Such errors got treated as Bugs in manual testing.
5. Failure-
A failure indicates a fatal issue in software or in its module which is making the system inoperative or unresponsive. Such an error in the software which the end customer reports are a Failure. The manual testers also discover many failures during the development cycle.
6. Fault-
A fault makes an application behave in a wrong manner.
The problems like an invalid step, lack of resources or inappropriate data definition could cause a fault in a program. It may happen in software because the developer has not added the code for fault tolerance.
Summary – Points to Ponder
We provided the definition of Wrong, Miss, Error, Bug, Failure, and Fault in a simplistic manner. However, some of you could have a different perception of these terms. Please feel free to send your views to us and make these more realistic for the testing fraternity.
July 15, 2020
If a tester is testing a software, s/he might come across several terms like failure, defect, bugs, mistakes, fault, error, etc., which are used by them interchangeably. However, have you ever wondered, whether these terms are synonyms of one another or do they specify different aspects of software testing process? Well, as an answer to this question, here is a detailed differentiation of all these terms, which will help us differentiate them from one another.
What is the Difference between Error, Mistake, Fault, Bug, Failure, & Defect?
The terms- error, mistakes, faults, bugs, failures, and defects are used interchangeably by the majority of people around the world, but they signify and represent different aspects of the software. These terms are an integral part of the software testing process and without detecting and identifying them the team of testers cannot validate the quality, effectiveness, functionality, and more of the software.
All these discrepancies impact the system differently, have a distinctive quality and are thoroughly different from one another. From the reason of their occurrence in the software to the steps taken to prevent them, majority of the aspects related to these terms are different. Therefore, to help you understand the difference between these components of the software, here is a detailed discussion on the same.
Error & Mistake:
During the process of software testing, errors are the most basic discrepancies found by the team of testers. These are the mistakes made by the software developer or programmer, while preparing the code or design of the software. Errors are mainly a deviation from the results expected by the team, which further changes the functionality of the software.
Reasons Error & Mistakes:
The reasons for these errors and mistakes are misconceptions or misunderstanding on the part of the software developer. Other reasons for errors and mistakes in the software are:
- Because of wrong login, loop, and syntax.
- Mistakes in the program.
- Confusion in understanding the requirements of the software.
- Miscalculation of some values.
- Misinterpretations and issues in coding.
- If a developer is unable to successfully compile or run a program.
- Mistakes in design or requirement activities.
- Discrepancy between actual and expected results.
Ways to Prevent Errors & Mistakes:
- Improve software quality with code and system review.
- Identify issues and prepare appropriate mitigation plan.
- Verify fixes and validate their quality and accuracy.
- Indulge in thorough testing.
- Adopt effective software development methodologies.
Fault:
Introduced in the software because of an error, fault is another discrepancy found by the team of testers during the process of software testing. Unlike error, the reason for a fault to occur while implementing the software is not because of a miscalculation of some value or discrepancy between actual and expected result, but is merely a manifestation of an error in a software. Moreover, a fault in the software system inhibits it from performing its intended function and forces the system to act in an unanticipated manner.
Reasons for Faults:
Faults in a system can be raised because of various reasons, few of which are mentioned here:
- Discrepancy or issue in the code that causes the failure of the system/program.
- Caused by an introduction of an incorrect step, process, or data definition.
- An anomaly or irregularity in the software, which makes the software behave in an incorrect way and not as per the stated requirements.
Ways to Prevent Faults:
- Implementing thorough code analysis.
- Peer review.
- Measure functional requirements.
- Validate the accuracy of software design and programming.
Bugs:
Bugs are the most integral part of a software system and can be termed as the errors, flaws, and faults present in the computer program that impact the performance as well as the functionality of the software can cause it to deliver incorrect and unexpected results. These not only impact the performance of the software, but also cause it to behave in an unanticipated way.
Reasons for Bugs:
From errors and mistakes made in the source code of the software, to issues and flaws found in the software design, the reasons for bugs to be introduced in the software system can be many, which are defined below:
- Error or flaw found in the development environment of the software.
- Issue in the software or hardware that leads it to malfunction.
- Discrepancies in the Operating System used by the program.
- Few bugs are even caused due to incorrect codes produced by compilers.
Ways to Prevent Bugs:
- Adapting innovative and effective development methodologies.
- Offering programming language support.
- Analyzing the code thoroughly.
- Test-driven development.
.png)
Failure:
When a software is incapable of performing the required functions and is offering results that are not adequate and far from the expected results, then it is termed as a failure. These failures are incorrect external behaviour that leads a software to deliver services that are not in compliance with the specifications.
Reasons for Failures:
Failures usually occur when a defect present in the system is executed by the team, which forces it to produce unpredicted and unanticipated results and function inappropriately. Other reasons that lead to the failure of the software are:
- Human Error: Errors and mistakes made by the human while interacting with the software and by providing wrong or incomplete inputs.
- Environmental Conditions: Another common reason that forces the system to fail are the environment conditions. These impact the hardware and force it to fail. Additionally, it changes the various environment variables.
- Users: Failures may also occur in the system if the user tries to perform operations that can harm the functionality of the software. Moreover, they can also execute actions with the intention of breaking the system, which will further lead to failures.
- System Usage: Failures might also arise due to errors in the way system is being used.
Ways to Prevent Failures:
- Identify and analyze errors and issues.
- Adopt effective preventive techniques.
- Ensure re-testing.
- Revise and revisit specifications and requirements.
Defect:
If the actual result of the software deviates from the one expected and anticipated by the team of testers, while testing the software, then it results into a defect. Defects, are therefore, defined as any deviation or irregularity from the specifications mentioned in the product functional specification document by the client or any other stakeholders of the project. These are the discrepancies and issues in the software, found during the process of testing, that impact its functionality. Moreover, defects are errors found after the application goes into product.
Reasons for Defects:
Defects in the software can hinder the functionality as well as the performance of the software. Hence, it is important for us to know the various reasons that cause defects to occur in the system, some of which are mentioned below:
- An error in coding or logic that impacts the software and causes it to malfunction or perform in an inaccurate manner.
- Any deviation from the customer requirements also leads to defects in the software.
- Troubles and mistakes in the external behaviour and internal structure and design.
- Providing wrong and inaccurate inputs.
Ways to Prevent Defects:
- Peer review.
- Adopting various efficient programming techniques.
- Performing regular code reviews to assess its quality and accuracy.
- Use of effective and accurate software development methodologies.
.png)
.png)
Difference between Error, Mistake, Fault, Bug, Failure, & Defect Infographics:
Dont Forget to share our Infographics
Conclusion :
With the assistance of above discussion, we can easily conclude that the various issues and discrepancies found during the process of software are interdependent and connected to each other. Usually, occurrence of one leads to the introduction of other, which together impacts the functionality of the software and leads it to deliver unexpected results and services, which are not in compliance with the specified requirements. Though all these discrepancies- errors, mistakes, faults, bugs, failures, and defects —hamper the quality and performance of the software, but they influence and modify different parts of the software and vary from one another immensely.

















.png)
